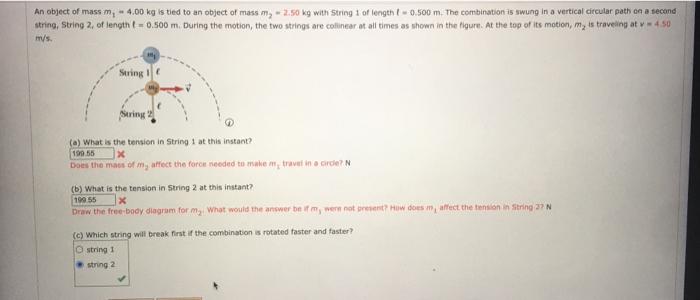
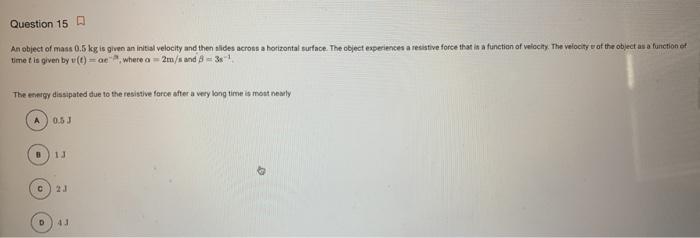
An object has a mass of 13.5 kilograms – An object with a mass of 13.5 kilograms serves as a tangible example to delve into the profound concept of mass in physics. Mass, a fundamental property of matter, plays a pivotal role in shaping our understanding of the universe, from the motion of celestial bodies to the interactions of subatomic particles.
This comprehensive exploration will unravel the intricacies of mass, its measurement techniques, and its diverse applications. We will examine the relationship between mass and gravity, unravel the law of conservation of mass, and explore the variations in mass measurements across different contexts.
Physical Properties of Mass

Mass is a fundamental property of matter that measures the amount of substance in an object. It is a scalar quantity, meaning it has only magnitude and no direction. Mass is an important concept in physics as it plays a crucial role in determining the behavior of objects in motion and under the influence of forces.
SI Unit of Mass
The International System of Units (SI) defines the kilogram (kg) as the base unit of mass. One kilogram is equal to the mass of the International Prototype Kilogram, a cylinder made of platinum-iridium alloy stored at the International Bureau of Weights and Measures in France.
Relationship to Other Units
The kilogram is related to other units of mass through the following conversions:
- 1 kilogram = 1000 grams (g)
- 1 kilogram = 2.2046 pounds (lb)
- 1 kilogram = 0.0685 slugs
Difference Between Mass and Weight
Mass and weight are often used interchangeably, but they are distinct concepts. Mass is an intrinsic property of an object, while weight is the force exerted on an object due to gravity. Weight is dependent on the gravitational field strength, which varies depending on the location of the object.
In contrast, mass remains constant regardless of the gravitational field.
Measuring Mass
Mass can be measured using a variety of methods, including:
Mechanical Scales
Mechanical scales use a balance beam to compare the mass of an object to a known mass. The most common type of mechanical scale is the triple-beam balance.
Electronic Scales, An object has a mass of 13.5 kilograms
Electronic scales use strain gauges or load cells to measure the force exerted by an object on a platform. Electronic scales are more precise and accurate than mechanical scales.
Accuracy and Precision
The accuracy of a mass measurement refers to how close the measured value is to the true value. The precision of a mass measurement refers to how repeatable the measurement is. Electronic scales are typically more accurate and precise than mechanical scales.
Factors Affecting Accuracy
Several factors can affect the accuracy of mass measurements, including:
- Calibration of the scale
- Environmental conditions (e.g., temperature, humidity)
- Operator technique
- Type of object being measured
Applications of Mass Measurement
Mass measurement is used in a wide variety of applications, including:
Commerce
Mass is used to determine the price of goods sold by weight, such as produce, meat, and grains.
Medicine
Mass is used to determine the dosage of medications and to monitor weight gain or loss.
Engineering
Mass is used to calculate the strength and stability of structures, design vehicles, and determine the fuel efficiency of engines.
Scientific Research
Mass is used in a wide range of scientific research, including studies of the composition of materials, the motion of objects, and the properties of gravity.
Safety
Mass measurement is used to ensure the safe operation of vehicles, aircraft, and other equipment.
Mass and Gravity
Mass is closely related to gravity. The force of gravity between two objects is directly proportional to the product of their masses. This relationship is described by Newton’s law of universal gravitation:
F = Gm₁m₂/r²
where:
- F is the force of gravity
- G is the gravitational constant (6.674 × 10^-11 N m²/kg²)
- m₁ and m₂ are the masses of the two objects
- r is the distance between the centers of mass of the two objects
Implications
The relationship between mass and gravity has several important implications:
- Objects with greater mass experience a greater force of gravity.
- The force of gravity is responsible for holding planets in orbit around the sun and moons in orbit around planets.
- The force of gravity is what causes objects to fall to the ground.
Conservation of Mass
The law of conservation of mass states that the total mass of an isolated system remains constant, regardless of the changes that occur within the system. This law is a fundamental principle of physics and has been experimentally verified in numerous experiments.
Implications
The law of conservation of mass has several important implications:
- Chemical reactions do not create or destroy mass, but rather rearrange the atoms and molecules present.
- The universe is a closed system, meaning that no mass can enter or leave the universe.
- The law of conservation of mass is one of the foundations of modern chemistry and physics.
Mass in Different Contexts: An Object Has A Mass Of 13.5 Kilograms

The concept of mass is used in a variety of contexts beyond mechanics and gravity, including:
Fluid Mechanics
In fluid mechanics, mass is used to calculate the density and buoyancy of fluids.
Thermodynamics
In thermodynamics, mass is used to calculate the heat capacity and specific heat of substances.
Special Relativity
In special relativity, mass is used to calculate the relativistic energy of an object.
FAQ Overview
What is the difference between mass and weight?
Mass is a measure of the amount of matter in an object, while weight is a measure of the force exerted on an object due to gravity. Mass is an intrinsic property of an object, whereas weight can vary depending on the gravitational field it is in.
How is mass measured?
Mass can be measured using a variety of methods, including mechanical scales, electronic scales, and balances. The accuracy and precision of mass measurements depend on the specific technique used.
What are some applications of mass measurement?
Mass measurement is used in a wide range of applications, including commerce, medicine, engineering, and scientific research. It is essential for ensuring accuracy and safety in various industries.
