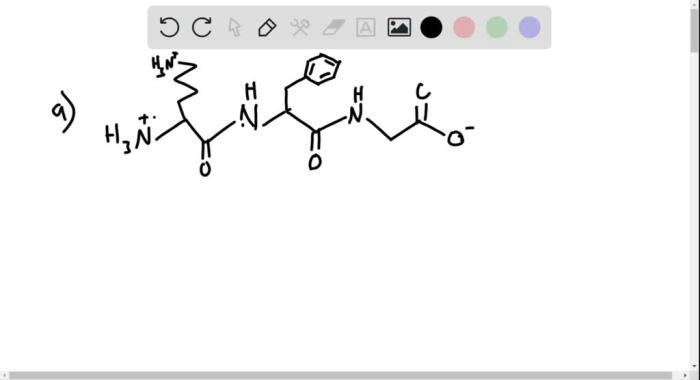
Condensed structural formula for the tripeptide – The condensed structural formula for a tripeptide is a concise representation of its molecular structure. It provides a systematic and efficient way to describe the arrangement and connectivity of amino acids within a tripeptide, enabling a deeper understanding of its structure-function relationships and facilitating various applications in peptide chemistry and biology.
This guide delves into the components, structural representation, stereochemistry, and applications of condensed structural formulas for tripeptides, offering a comprehensive overview of this essential tool in peptide science.
Introduction
A condensed structural formula for a tripeptide is a concise representation of the molecule’s structure, showing the sequence of amino acids and the peptide bonds that connect them. These formulas are widely used in biochemistry and chemistry to describe tripeptides and larger peptides.
Components of a Condensed Structural Formula: Condensed Structural Formula For The Tripeptide
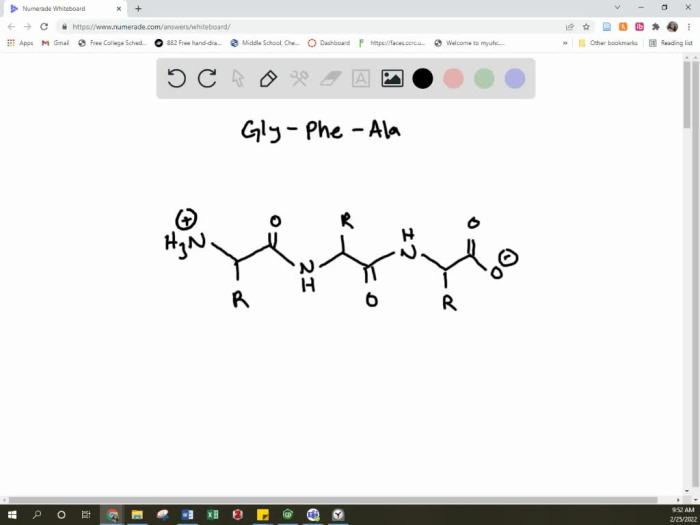
A condensed structural formula for a tripeptide consists of three amino acids, each represented by a one-letter code. The amino acids are connected by peptide bonds, which are indicated by a dash (-). For example, the tripeptide Ala-Ser-Gly is composed of the amino acids alanine (Ala), serine (Ser), and glycine (Gly), connected by two peptide bonds.
Structural Representation, Condensed structural formula for the tripeptide
The condensed structural formula for Ala-Ser-Gly is:H2N-Ala-Ser-Gly-COOHIn this formula, the amino acids are arranged from left to right in the order of their sequence. The N-terminus (amino group) of the first amino acid is on the left, and the C-terminus (carboxyl group) of the last amino acid is on the right.
Stereochemistry
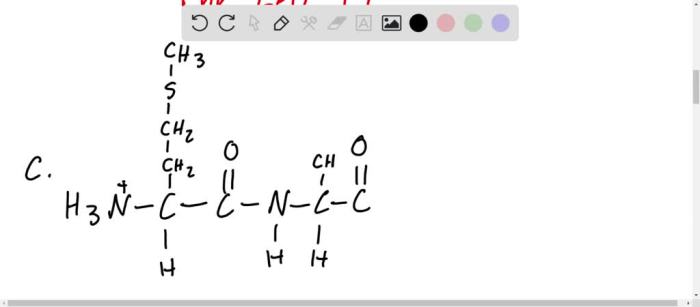
Amino acids can exist in two different stereochemical configurations, designated as D and L. The stereochemistry of an amino acid in a condensed structural formula is indicated by a prefix, such as D-Ala or L-Ser. For example, the tripeptide D-Ala-L-Ser-Gly represents a tripeptide in which the first amino acid (alanine) has the D configuration, the second amino acid (serine) has the L configuration, and the third amino acid (glycine) has no chiral center.
Applications of Condensed Structural Formulas
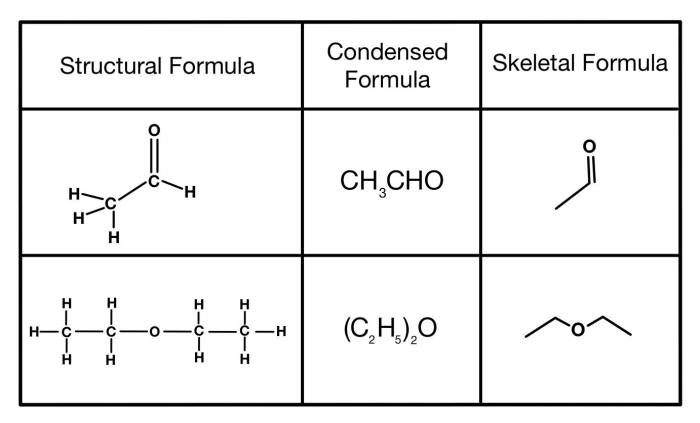
Condensed structural formulas are widely used in peptide synthesis, as they provide a clear and concise representation of the desired peptide sequence. They are also essential for understanding peptide structure-function relationships, as the sequence of amino acids determines the peptide’s biological activity.
Additionally, condensed structural formulas are used in peptide databases and cheminformatics, where they facilitate the storage, retrieval, and analysis of peptide data.
Question & Answer Hub
What is the purpose of a condensed structural formula for a tripeptide?
The condensed structural formula provides a concise and systematic representation of the molecular structure of a tripeptide, facilitating the understanding of its structure-function relationships and enabling various applications in peptide chemistry and biology.
How are amino acids represented in a condensed structural formula?
Amino acids are represented using one-letter codes, which are standardized abbreviations for their full names. For example, Alanine is represented by “A”, Serine by “S”, and Glycine by “G”.
What do the peptide bonds in a condensed structural formula represent?
Peptide bonds are represented by lines connecting the alpha-carbon atoms of adjacent amino acids, indicating the covalent bonds that link them together to form the peptide backbone.