Which of the following statements is true of narcolepsy? Narcolepsy is a chronic neurological disorder that affects the brain’s ability to control sleep-wake cycles, leading to excessive daytime sleepiness (EDS) and other debilitating symptoms. This article delves into the complexities of narcolepsy, exploring its definition, symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatment options, and the impact it has on daily life.
Narcolepsy is a multifaceted condition that can manifest in various forms, with each type presenting unique characteristics. Understanding the nuances of narcolepsy is crucial for effective management and support for individuals affected by this disorder.
Definition of Narcolepsy

Narcolepsy is a chronic neurological disorder characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness (EDS) and other symptoms such as cataplexy, sleep paralysis, hypnagogic hallucinations, and automatic behaviors. It is a disabling condition that can significantly impact an individual’s daily life.
Key Characteristics of Narcolepsy, Which of the following statements is true of narcolepsy
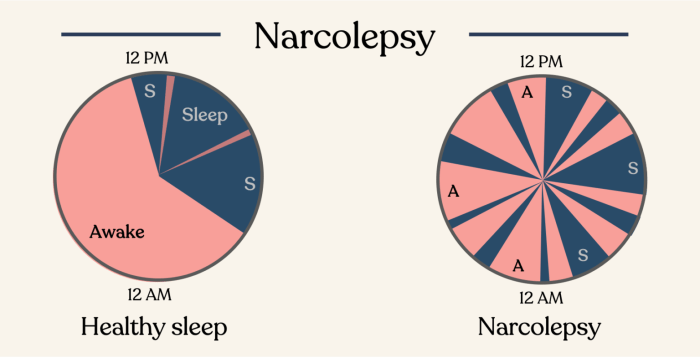
- Excessive daytime sleepiness (EDS): Irresistible urge to sleep during the day, often at inappropriate times.
- Cataplexy: Sudden loss of muscle tone triggered by emotions such as laughter, surprise, or anger.
- Sleep paralysis: Temporary inability to move or speak upon waking or falling asleep.
- Hypnagogic hallucinations: Vivid, dream-like experiences that occur while falling asleep.
- Automatic behaviors: Unconscious, repetitive actions performed while in a state of drowsiness.
Types of Narcolepsy
- Type 1 narcolepsy: Characterized by EDS and cataplexy.
- Type 2 narcolepsy: Characterized by EDS without cataplexy.
Questions Often Asked: Which Of The Following Statements Is True Of Narcolepsy
What are the key characteristics of narcolepsy?
Narcolepsy is characterized by excessive daytime sleepiness (EDS), cataplexy (sudden loss of muscle tone triggered by emotions), sleep paralysis (temporary inability to move or speak upon waking or falling asleep), and hypnagogic/hypnopompic hallucinations (vivid, dream-like experiences during the transition to or from sleep).
What causes narcolepsy?
Narcolepsy is primarily caused by a deficiency of hypocretin (orexin), a neurotransmitter that regulates sleep-wake cycles. This deficiency can be genetic or acquired through factors such as head injuries or infections.
How is narcolepsy diagnosed?
Narcolepsy is diagnosed based on a combination of symptoms and specialized sleep studies, such as polysomnography (PSG) and multiple sleep latency test (MSLT), which assess sleep patterns and measure daytime sleepiness.