Write the condensed electron configurations for the lu atom – Delving into the fascinating realm of atomic structure, we embark on a journey to unravel the condensed electron configuration of the lutetium atom, a crucial concept that unlocks insights into its chemical behavior and properties.
The condensed electron configuration serves as a concise representation of the electron distribution within an atom, providing valuable information about its valence electrons and oxidation states. By exploring the case of the lutetium atom, we gain a deeper understanding of the periodic trends and electronic characteristics that shape the behavior of elements.
Introduction to Condensed Electron Configuration: Write The Condensed Electron Configurations For The Lu Atom
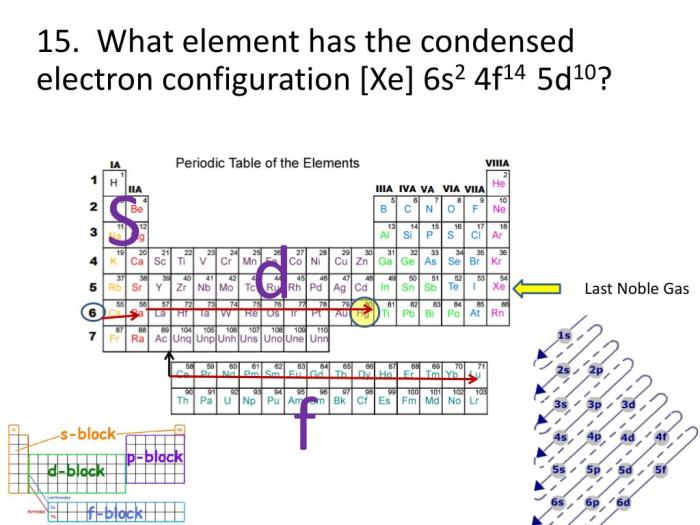
A condensed electron configuration is a shorthand notation that describes the electron distribution of an atom or ion. It provides a simplified representation of the electron configuration by grouping electrons in their respective energy levels and using noble gas core notation.
Noble gas core notation involves representing the core electrons of an atom using the electron configuration of the nearest noble gas. This helps simplify the notation and focus on the valence electrons, which are the electrons in the outermost energy level that participate in chemical reactions.
Condensed Electron Configuration of Lu Atom
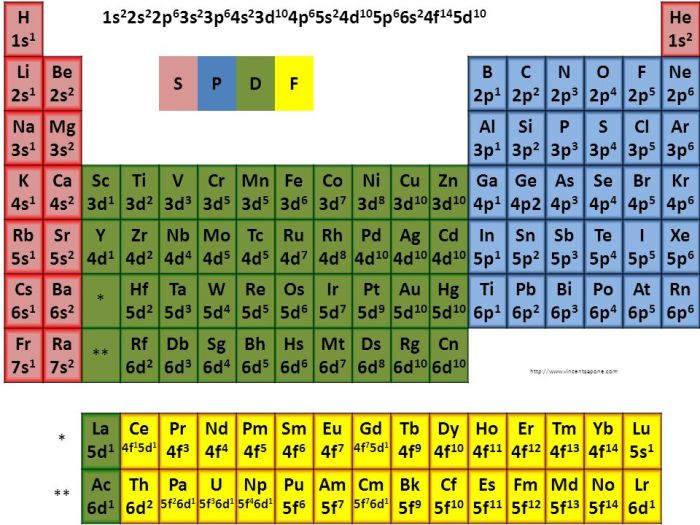
The atomic number of Lu is 71, indicating that it has 71 electrons. Its condensed electron configuration is:
[Xe] 4f145d 16s 2
This configuration is determined by first identifying the nearest noble gas, which is Xe (xenon) with an atomic number of 54. The electron configuration of Xe is [Xe] 5s 25p 6. The electrons in these orbitals are considered core electrons and are represented by [Xe].
The remaining electrons in Lu are distributed in the 4f, 5d, and 6s orbitals. The 4f orbital is filled with 14 electrons, the 5d orbital has 1 electron, and the 6s orbital has 2 electrons. This results in the condensed electron configuration [Xe] 4f 145d 16s 2.
Valence Electrons and Oxidation States, Write the condensed electron configurations for the lu atom
The valence electrons of an atom are the electrons in the outermost energy level. In the case of Lu, it has two valence electrons in the 6s orbital.
Based on its condensed electron configuration, Lu can exhibit various oxidation states. The most common oxidation states are +2 and +3. The +2 oxidation state is achieved by losing the two valence electrons, while the +3 oxidation state is achieved by losing the two valence electrons and one of the 5d electrons.
Applications of Condensed Electron Configuration
Condensed electron configuration plays a crucial role in predicting the chemical properties of an element. It helps determine:
- The number of valence electrons, which influences the element’s reactivity and bonding behavior.
- The possible oxidation states, which are important for understanding the element’s chemical reactions.
- The magnetic properties, as the number of unpaired electrons in the d or f orbitals determines the element’s magnetic behavior.
Condensed electron configuration is widely used in various fields of chemistry, including:
- Predicting the reactivity of elements and their tendency to form compounds.
- Understanding the bonding behavior and molecular structures of compounds.
- Explaining the magnetic properties of materials.
Comparison with Other Lanthanides

Lu is a member of the lanthanide series, which consists of elements with atomic numbers 57 to 71. All lanthanides have similar condensed electron configurations, with the valence electrons being in the 4f and 5d orbitals.
The condensed electron configuration of Lu, [Xe] 4f 145d 16s 2, is similar to that of other lanthanides. However, the number of 4f electrons varies across the series, resulting in different chemical properties and oxidation states.
FAQ Section
What is the condensed electron configuration of the lutetium atom?
The condensed electron configuration of the lutetium atom is [Xe] 4f 145d 16s 2.
How many valence electrons does the lutetium atom have?
The lutetium atom has three valence electrons.
What are the common oxidation states of lutetium?
The common oxidation states of lutetium are +2 and +3.